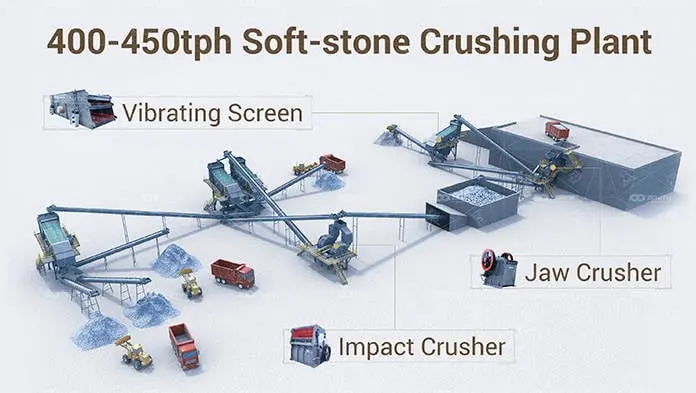
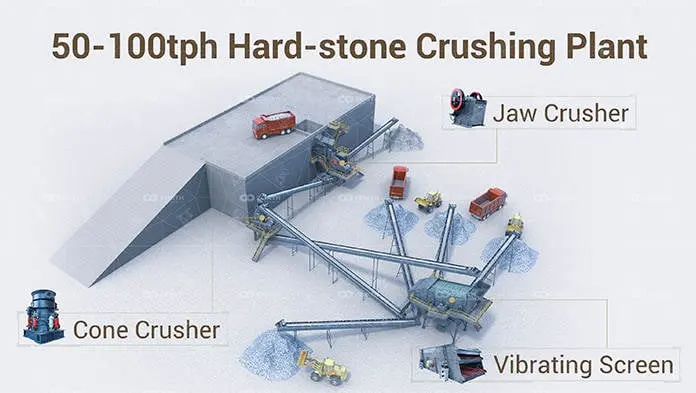
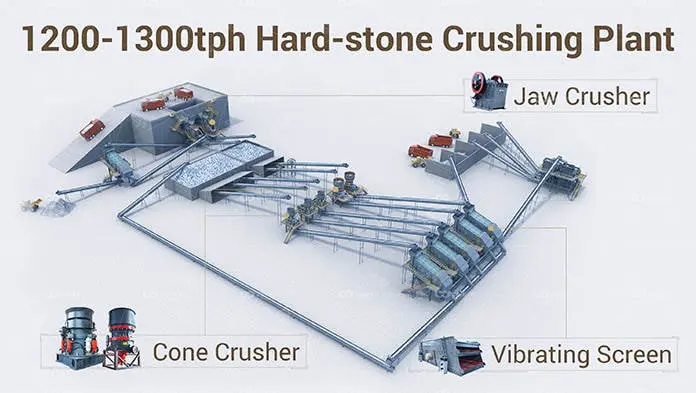
What is a tertiary crusher
Time:12 September 2025

A tertiary crusher is an essential component in the aggregate production process, designed to further reduce the size of materials after they have been processed by primary and secondary crushers. This article explores the purpose, types, and applications of tertiary crushers in the mining and construction industries.
Purpose of Tertiary Crushers
Tertiary crushers are used to achieve finer material sizes and are typically employed in the final stage of the crushing process. They help in:
- Enhancing product quality: By producing smaller, uniform-sized particles, tertiary crushers improve the quality of the final product.
- Increasing efficiency: They allow for better control over the size and shape of the output, optimizing downstream processes.
- Meeting specific requirements: Certain projects require specific particle sizes, which tertiary crushers can provide.
Types of Tertiary Crushers
There are various types of tertiary crushers, each suited for different applications and material characteristics. The most common types include:
Cone Crushers
Cone crushers are popular for their ability to crush hard and abrasive materials. They work by compressing the material between a stationary piece and a moving piece, which rotates around a central axis.
– High efficiency and low operational costs
– Ability to produce a uniform particle size
– Suitable for a wide range of materials
Impact Crushers
Impact crushers utilize the force of impact to break down materials. They are ideal for softer, less abrasive materials and can produce a more cubical shape.
– High reduction ratios
– Ability to handle large feed sizes
– Versatile applications
Vertical Shaft Impact (VSI) Crushers
VSI crushers use a high-speed rotor to throw materials against a hard surface, breaking them into smaller pieces. They are particularly effective for producing sand and fine aggregates.
– Produces high-quality, cubical-shaped particles
– Excellent for sand production
– Energy-efficient
Applications of Tertiary Crushers
Tertiary crushers are widely used in various industries, including:
- Mining: To process ores and minerals, ensuring the desired size for further processing or direct use.
- Construction: In the production of aggregates for concrete and asphalt, where specific particle sizes are required.
- Recycling: To break down materials like concrete and asphalt for reuse in new projects.
Selection Criteria for Tertiary Crushers
Choosing the right tertiary crusher involves considering several factors:
- Material characteristics: Hardness, abrasiveness, and moisture content can affect crusher performance.
- Desired output size: The crusher must be capable of achieving the required particle size.
- Capacity requirements: The crusher should meet the production demands of the operation.
- Operational costs: Energy consumption, maintenance needs, and wear parts should be evaluated.
Conclusion
Tertiary crushers play a crucial role in the aggregate production process, providing the final reduction in material size necessary for high-quality end products. Understanding the different types and applications of tertiary crushers can help operators make informed decisions, optimizing efficiency and meeting specific project requirements. Whether in mining, construction, or recycling, tertiary crushers are indispensable tools in the modern industrial landscape.