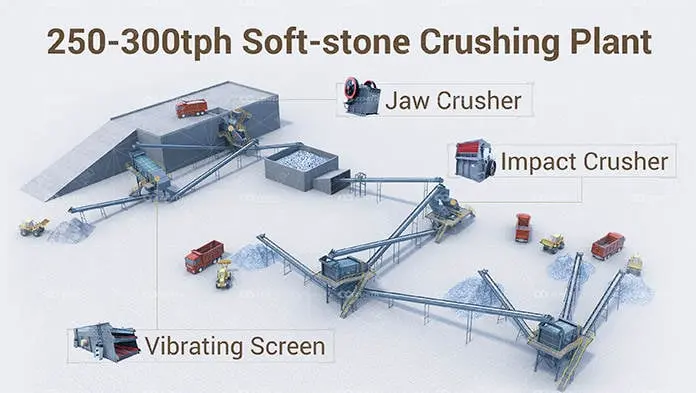
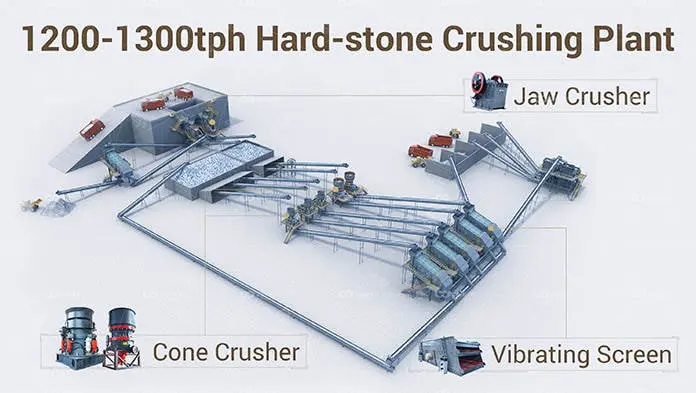
What is a ball mill
Time:12 September 2025

A ball mill is a type of grinder used to grind and blend materials for use in mineral dressing processes, paints, pyrotechnics, ceramics, and selective laser sintering. It works on the principle of impact and attrition: size reduction is done by impact as the balls drop from near the top of the shell.
Overview
Ball mills are used extensively in the mechanical alloying process in which they are not only used for grinding but for cold welding as well, with the purpose of producing alloys from powders. The ball mill is a key piece of equipment for grinding crushed materials, and it is widely used in production lines for powders such as cement, silicates, refractory material, fertilizer, glass ceramics, etc., as well as for ore dressing of both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Components of a Ball Mill
A ball mill typically consists of:
- Shell: The cylindrical shell is filled with grinding media, usually steel balls.
- Grinding Media: The balls which do the grinding by falling onto the material.
- Feed: The material to be ground is fed into the shell.
- Discharge: The ground material is discharged from the shell.
Types of Ball Mills
Ball mills can be classified into several types based on their operation and design:
1. Horizontal Ball Mills
These are the most common type of ball mills. They are typically used for grinding materials that are not too hard.
2. Vertical Ball Mills
These are used for applications where a finer product is required. They are less common than horizontal ball mills.
3. Planetary Ball Mills
These are smaller and are used for mixing and grinding purposes. They are particularly useful for laboratory applications.
Working Principle
The ball mill operates on the principle of impact and attrition:
- Impact: The grinding media (balls) fall from near the top of the shell.
- Attrition: The balls grind the material by rolling it between each other.
Applications
Ball mills are used in various industries for a wide range of applications:
- Mineral Dressing: Used for grinding ores to liberate valuable minerals.
- Paints and Pigments: Used for grinding and mixing pigments.
- Ceramics: Used for grinding raw materials to produce ceramic products.
- Pyrotechnics: Used for grinding chemicals to produce fireworks.
Advantages of Ball Mills
Ball mills offer several advantages:
- Efficiency: They can achieve a high degree of fineness.
- Versatility: Suitable for both wet and dry grinding processes.
- Scalability: Can be used for small-scale laboratory applications or large-scale industrial processes.
Disadvantages of Ball Mills
Despite their advantages, ball mills also have some drawbacks:
- Energy Consumption: They can be energy-intensive.
- Wear and Tear: The grinding media and liners can wear out over time.
- Noise: They can be noisy during operation.
Conclusion
Ball mills are essential tools in various industries for grinding and blending materials. Their ability to produce fine particles makes them indispensable in mineral processing, ceramics, and other applications. Understanding the different types, components, and working principles of ball mills can help in selecting the right equipment for specific needs.