What is the production process of stone aggregates
Time:12 September 2025

Stone aggregates are essential materials used in construction and various civil engineering projects. They are primarily used in the construction of roads, bridges, and buildings. Understanding the production process of stone aggregates is crucial for ensuring high-quality materials that meet industry standards.
Overview of Stone Aggregates
Stone aggregates are crushed stone materials that are used in construction. They are produced by mining suitable rock deposits and breaking down the rocks to the desired size. The production process involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product.
Stages of Stone Aggregate Production
The production process of stone aggregates can be broken down into several key stages:
- Extraction
- Crushing
- Screening
- Washing
- Storage and Transportation
1. Extraction
The first step in the production of stone aggregates is the extraction of raw materials from quarries or mines.
- Site Selection: The location of the quarry is chosen based on the availability of high-quality rock deposits.
- Drilling and Blasting: Once a suitable site is selected, drilling and blasting are used to break the rock into manageable pieces.
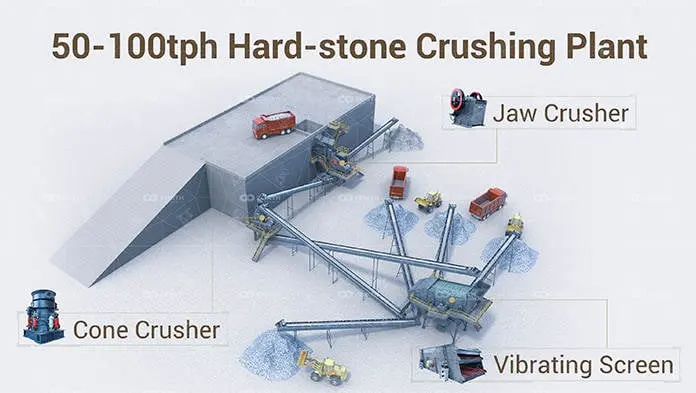
2. Crushing
After extraction, the raw stone material is transported to a crushing facility where it undergoes several crushing stages:
- Primary Crushing: Large rocks are fed into a primary crusher, which reduces them to smaller, more manageable sizes.
- Secondary Crushing: The output from the primary crusher is further reduced in size by secondary crushers.
- Tertiary Crushing: For finer aggregates, tertiary crushers are used to achieve the desired size.
3. Screening
Screening is a critical step that ensures the aggregates are of uniform size and quality:
- Vibrating Screens: The crushed material is passed through vibrating screens to separate it into different size fractions.
- Quality Control: Regular checks are performed to ensure that the aggregates meet specified standards.
4. Washing
Washing is an optional step but is often necessary to remove impurities such as clay, silt, and dust:
- Washing Equipment: Equipment like log washers and sand classifiers are used to clean the aggregates.
- Water Recycling: Water used in the washing process is often recycled to minimize environmental impact.
5. Storage and Transportation
Once the aggregates are processed, they are stored and prepared for transportation:
- Stockpiling: Aggregates are stockpiled in designated areas to prevent contamination and ensure easy access.
- Loading and Transport: The aggregates are loaded onto trucks or conveyor belts for transport to construction sites or customers.
Quality Control in Aggregate Production
Ensuring the quality of stone aggregates is crucial for the success of construction projects. Quality control measures include:
- Regular Testing: Samples of aggregates are regularly tested for size, shape, and strength.
- Process Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the production process helps identify and rectify issues promptly.
- Compliance with Standards: Aggregates must comply with industry standards and specifications to be deemed suitable for use.
Environmental Considerations
The production of stone aggregates has several environmental impacts:
- Dust and Noise Pollution: Crushing and screening operations generate dust and noise, which need to be managed.
- Land Disturbance: Quarrying activities can lead to habitat destruction and landscape changes.
- Water Usage: The washing process requires significant amounts of water, necessitating efficient water management practices.
Conclusion
The production process of stone aggregates is a complex and multi-stage operation that requires careful planning and execution. From extraction to transportation, each step is crucial in ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product. By adhering to industry standards and implementing effective quality control measures, producers can supply high-quality aggregates that meet the demands of the construction industry.