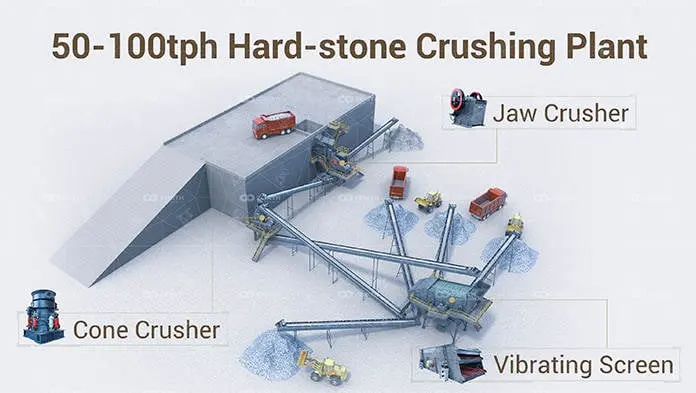
What is the difference between an impact, cone, and jaw crusher
Time:12 September 2025

Crushers are essential equipment in the mining and aggregate industries, used to reduce the size of rocks and other materials. Among the various types of crushers, impact crushers, cone crushers, and jaw crushers are the most commonly used. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right equipment for specific applications.
Overview of Crusher Types
Before diving into the differences, let’s briefly define each type of crusher:
- Impact Crusher: Utilizes impact force to break materials.
- Cone Crusher: Crushes materials between a gyrating cone and a fixed outer wall.
- Jaw Crusher: Uses compressive force to crush materials between two jaws.
Impact Crushers
Impact crushers are designed to handle materials with a high moisture content and are often used for secondary or tertiary crushing.
Characteristics
- Mechanism: Impact crushers operate by using the principle of quick impacts to crush materials.
- Design: Typically consists of a rotor with hammers or blow bars that rotate at high speeds.
- Output: Produces a more cubical product, suitable for road construction and other aggregate applications.
Advantages
- High reduction ratios: Can reduce materials to smaller sizes in a single pass.
- Versatile applications: Suitable for soft to medium-hard materials, including limestone and concrete.
- Adjustable settings: Allows for control over the size and shape of the output material.
Disadvantages
- Wear and tear: Parts such as hammers and blow bars can wear quickly, requiring frequent replacement.
- Lower efficiency: Not as efficient for very hard materials compared to cone crushers.
Cone Crushers
Cone crushers are typically used for secondary, tertiary, and quaternary crushing stages.
Characteristics
- Mechanism: Operates by compressing materials between a gyrating cone and a stationary outer wall.
- Design: Features a cone-shaped crushing chamber with a mantle and concave.
- Output: Produces a uniform product size, ideal for high-quality aggregate production.
Advantages
- High efficiency: Suitable for hard and abrasive materials, such as granite and basalt.
- Consistent product size: Produces a more uniform output compared to impact crushers.
- Low operational costs: Generally requires less maintenance and has longer wear life.
Disadvantages
- Limited versatility: Not ideal for materials with high moisture content or clay.
- Complex setup: Requires precise alignment and calibration for optimal performance.
Jaw Crushers
Jaw crushers are primarily used for the initial stage of crushing, known as primary crushing.
Characteristics
- Mechanism: Crushes materials by compressing them between two jaws—one fixed and one movable.
- Design: Features a V-shaped chamber with a fixed jaw and a movable jaw.
- Output: Produces a coarse product, often used as a precursor to secondary crushing.
Advantages
- Robust construction: Suitable for hard and abrasive materials, such as ores and rocks.
- Simple design: Easy to operate and maintain, with fewer moving parts.
- Versatile applications: Can handle a wide range of materials, including large boulders.
Disadvantages
- Lower reduction ratio: Typically requires additional crushing stages for finer output.
- Limited product shape: Produces less cubical products compared to impact crushers.
Comparison Summary
Here’s a quick comparison of the three types of crushers:
- Impact Crushers: Best for softer materials and producing cubical products; less efficient for hard materials.
- Cone Crushers: Ideal for hard materials and producing uniform products; less versatile for wet or clay-based materials.
- Jaw Crushers: Suitable for primary crushing of hard materials; requires additional stages for finer outputs.
Conclusion
Selecting the right crusher depends on the material characteristics, desired product size, and specific application requirements. Understanding the differences between impact, cone, and jaw crushers will help in making informed decisions to optimize crushing operations.